Understanding Moderate Rainfall Warnings
When meteorological agencies issue a moderate rainfall warning, it signals expected rainfall that, while not as severe as heavy or extreme rainfall events, can still pose significant challenges. These warnings are crucial for public safety and preparedness, particularly in areas prone to flooding or saturated ground. Understanding the dynamics behind these warnings, the meteorological patterns involved, and their potential impacts is essential for the general public and authorities responsible for disaster management and response.

The Science Behind the Warnings
Meteorologists use various tools and data sources to forecast weather conditions, including satellite imagery, radar data, weather stations, and atmospheric models. For a moderate rainfall warning to be issued, specific criteria must be met. These typically involve anticipated rainfall amounts reaching a threshold that is likely to affect communities but not severe enough to warrant a higher-level alert, such as a heavy rainfall warning. The thresholds vary by region, depending on typical weather patterns, topography, and the ability of the environment to absorb water.
Regional Variability
The impact of moderate rainfall can vary dramatically depending on the region. In urban areas, even moderate rainfall can lead to significant disruptions due to the impervious surfaces that increase runoff, overwhelming stormwater systems and leading to flash floods. In contrast, moderate rainfall might be beneficial in rural or agricultural regions, particularly in periods of drought or semi-arid conditions. However, if the soil is saturated, the same rain can cause erosion or crop damage, illustrating the nuanced nature of rainfall impact assessments.
Preparing for Moderate Rainfall
Preparation for moderate rainfall primarily involves being aware of the forecast and understanding local flood risks. Local governments often use these warnings to activate plans for potential flooding, ensuring that resources and emergency personnel are ready to respond if the situation escalates.

Public Safety Measures
For the public, preparation might include ensuring that drainage systems are clear of debris, checking on emergency supplies like batteries and water, and planning routes to avoid low-lying areas prone to flooding. Public information campaigns often accompany moderate rainfall warnings, offering advice on how to prepare and where to get real-time updates as the weather situation evolves.
Infrastructure Readiness
On a larger scale, municipalities may carry out inspections and maintenance on infrastructure critical to managing increased water loads. This includes stormwater management systems, levees, dams, and roadways prone to washouts. Ensuring these systems are in good condition before a storm can significantly reduce the risk of failure and the consequent impacts on communities.
Case Studies of Moderate Rainfall Events
Examining past moderate rainfall events can provide valuable lessons for future preparedness and response. These case studies highlight the importance of timely warnings and the effectiveness of pre-event planning and infrastructure resilience.
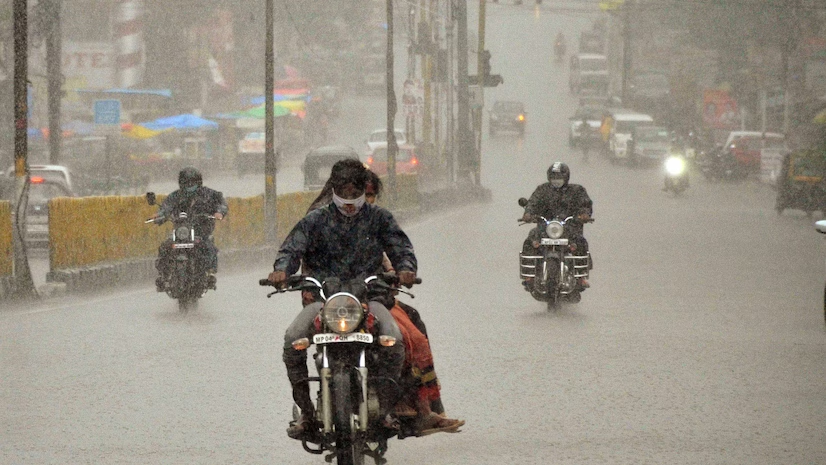

An Urban Example
In a recent moderate rainfall event in a central metropolitan area, the local government’s investment in upgraded drainage systems was credited with preventing significant flooding. The event, which delivered a third of the month’s typical rainfall in just 24 hours, tested the city’s infrastructure but resulted in minimal disruption thanks to recent improvements and proactive management.
A Rural Scenario
Conversely, a similar rainfall event in a rural area highlighted challenges such as road washouts and access issues for emergency services. The event underscored the need for better road infrastructure and more robust communication strategies to reach residents in remote areas during weather emergencies.

The Role of Climate Change
Broader climatic trends influence the frequency and intensity of moderate rainfall warnings. As the planet warms, the atmosphere holds more moisture, potentially increasing the volume of rainfall during storms. Understanding this link is crucial for long-term planning and adaptation strategies.
Adaptation Strategies
Communities are increasingly looking at ways to adapt to more frequent and intense rainfall, regardless of the warning level. This includes investing in green infrastructure, such as parks and wetlands that absorb excess water, and updating building codes to improve resilience to flooding.
Long-Term Forecasting Improvements
Meteorological agencies continue to improve their forecasting techniques, incorporating more data and refining models to provide more accurate and timely warnings. These advancements are vital in helping communities prepare for and respond to moderate rainfall events more effectively.

Conclusion
Moderate rainfall warnings are crucial in managing the risks associated with adverse weather conditions. Providing timely and accurate information, these warnings help individuals and communities make informed decisions to mitigate the impact of impending rainfall. Understanding and responding to these warnings becomes more critical in safeguarding lives and property as weather patterns evolve.